Weierstrass Function
Mathematical Definition
\[f(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \left [ \sum_{k=0}^{kmax} a^k \cos \left( 2 \pi b^k (x_i + 0.5) \right) - n \sum_{k=0}^{kmax} a^k \cos(\pi b^k) \right ] \]where $a \in (0,1)$, $b$ is a positive odd integer, and $k_{max}$ is a positive integer (commonly $a=0.5$, $b=3$, $k_{max}=20$).
Plots
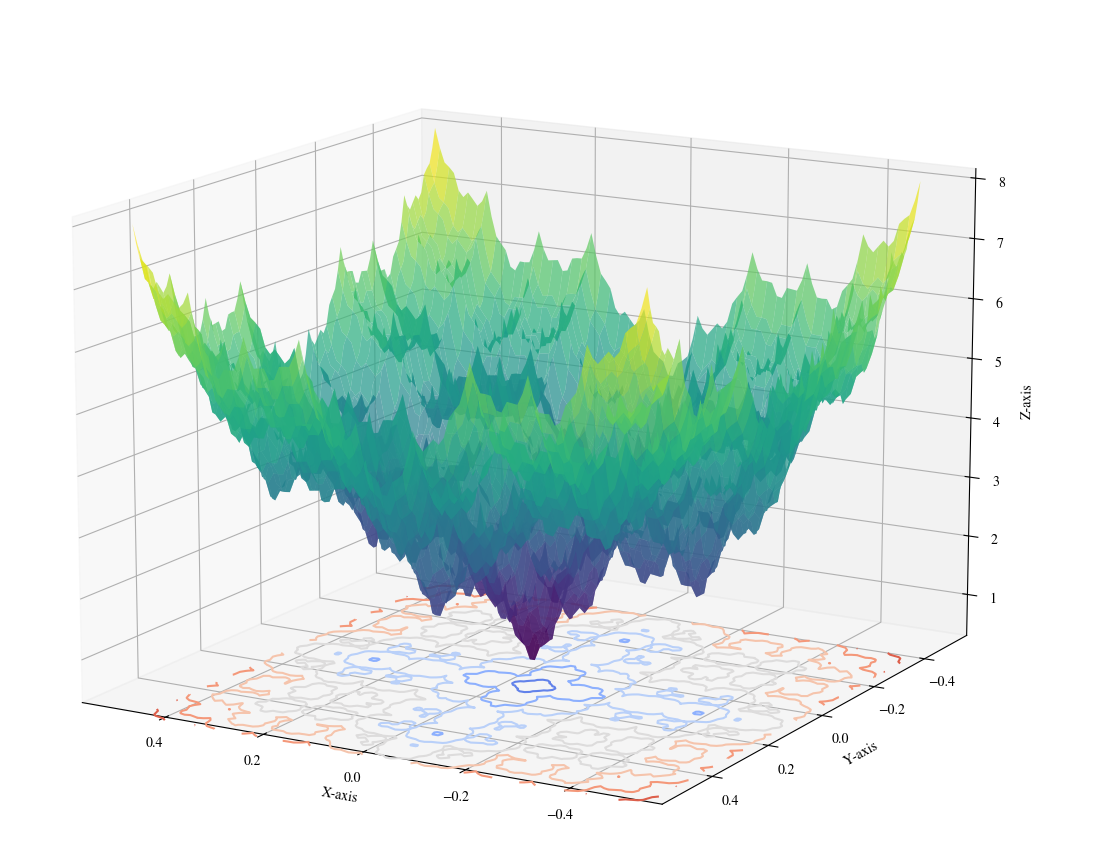
Description and Features
- The function is continuous but nowhere differentiable.
- The function is not convex.
- The function is defined on n-dimensional space.
- The function is multimodal.
- The function is separable.
Input Domain
The function is usually evaluated on the hypercube $x_i \in [-0.5, 0.5]$ for all $i = 1, …, n$.
Global Minimum
The global minimum is located at $\mathbf{x}^* = (0, …, 0)$, with
\[f(\mathbf{x}^*) = 0\]Implementation
Python
For Python, the function is implemented in the benchmarkfcns package, which can be installed from command line with pip install benchmarkfcns.
from benchmarkfcns import weierstrass
print(weierstrass([[0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1]]))MATLAB
An implementation of the Weierstrass Function with MATLAB is provided below.
% This function computes the Weierstrass function for each row of a matrix X,
% using a fully vectorized approach.
%
% Inputs:
% X: A matrix where each row is a vector of dimension n.
% a: A scalar parameter.
% b: A scalar parameter.
% kmax: An integer, the maximum value for k.
%
% Output:
% y: A column vector where each element is the result for the corresponding row of X.
function y = weierstrassfcn(X, a, b, kmax)
if nargin < 2
a = 0.5;
end
if nargin < 3
b = 3;
end
if nargin < 4
kmax = 20;
end
[num_rows, n] = size(X);
k = 0:kmax;
k_reshaped = reshape(k, 1, 1, []); % 1x1x(kmax+1)
X_reshaped = reshape(X + 0.5, num_rows, 1, n); % num_rows x 1 x n
b_powers = b .^ k;
term1_cos_input = 2 * pi * b_powers .* X_reshaped;
term1 = a .^ k .* cos(term1_cos_input); % num_rows x (kmax+1) x n
% Sum along the k dimension (the second dimension of term1)
sum_k_term1 = sum(term1, 2); % num_rows x 1 x n
sum_over_n = sum(sum_k_term1, 3); % num_rows x 1
sum_k_term2 = sum(a .^ k .* cos(pi * b .^ k));
y = sum_over_n - n * sum_k_term2;
endThe function can be represented in Latex as follows:
f(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \left [ \sum_{k=0}^{kmax} a^k \cos \left( 2 \pi b^k (x_i + 0.5) \right) - n \sum_{k=0}^{kmax} a^k \cos(\pi b^k) \right ] References
- Weierstrass function - Wikipedia
- Yao, X., Liu, Y., & Lin, G. (1999). Evolutionary programming made faster. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 3(2), 82-102.