Trid Function
Mathematical Definition
\[f(\mathbf{x})=\sum_{i=1}^{n}(x_i-1)^2-\sum_{i=2}^{n}(x_ix_{i-1})\]Plots
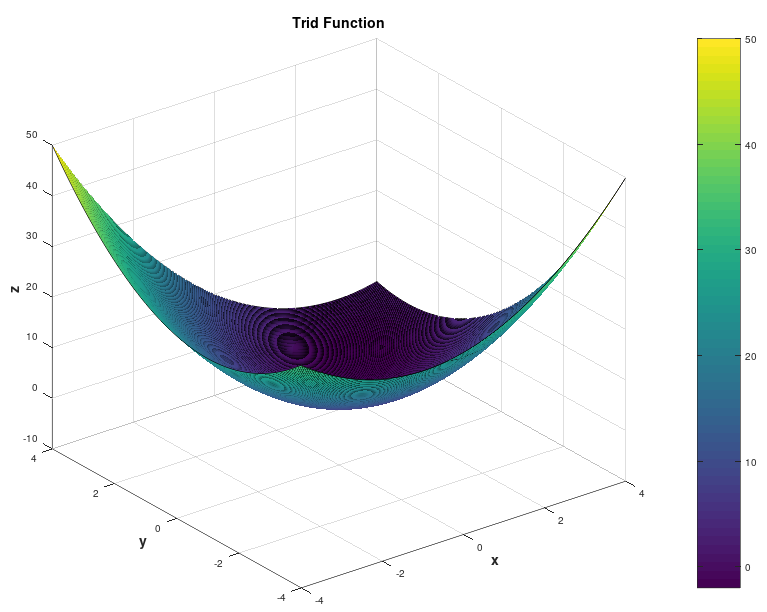
A contour of the function is presented below:
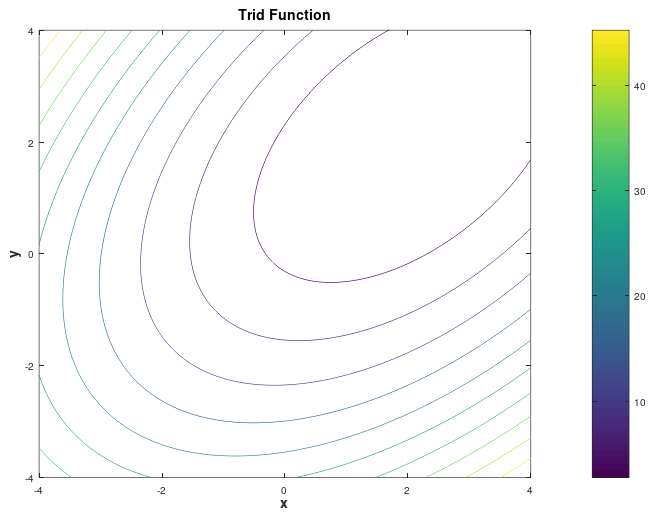
Description and Features
- The function is continuous.
- The function is convex.
- The function is defined on n-dimensional space.
- The function is unimodal.
- The function is differentiable.
- The function is non-separable.
Input Domain
The function can be defined on any input domain but it is usually evaluated on $x_i \in [-n^2, n^2]$ for $i=1, …, n$.
Global Minima
The function has one global minimum $f(\mathbf{x}^{\ast})=-n(n+4)(n-1)/6$ at ${x_i}^{\ast}=i(n+1 - i)$ for $i=1, …, n$.
Implementation
Python
For Python, the function is implemented in the benchmarkfcns package, which can be installed from command line with pip install benchmarkfcns.
from benchmarkfcns import trid
print(trid([[0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1]]))MATLAB
An implementation of the Trid Function with MATLAB is provided below.
% Computes the value of the Trid function.
% SCORES = TRIDFCN(X) computes the value of the Xin-She Yang
% function at point X. TRIDFCN accepts a matrix of size M-by-N and
% returns a vetor SCORES of size M-by-1 in which each row contains the
% function value for the corresponding row of X.
% For more information, please visit:
% benchmarkfcns.info/doc/tridfcn
%
% Author: Mazhar Ansari Ardeh
% Please forward any comments or bug reports to mazhar.ansari.ardeh at
% Google's e-mail service or feel free to kindly modify the repository.
function scores = tridfcn(x)
sum((x - 1) .^ 2, 2)
scores = sum((x - 1) .^ 2, 2) - sum(x(:, 2:end) .* x(:, 1:end-1), 2);
endThe function can be represented in Latex as follows:
f(\mathbf{x})=\sum_{i=1}^{n}(x_i-1)^2-\sum_{i=2}^{n}(x_ix_{i-1})References:
- http://www.sfu.ca/~ssurjano/trid.html.
- Adorio, E. P., & Diliman, U. P. MVF - Multivariate Test Functions Library in C for Unconstrained Global Optimization (2005).
- Global Optimization Test Problems http://www-optima.amp.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp/member/student/hedar/Hedar_files/TestGO.htm.